Targeted and accelerated digital transformation initiatives are gaining momentum and relevance to modernizing state and local government operations by adjusting to budget constraints, shifting resources to diversify revenues, and accelerating IT modernization.
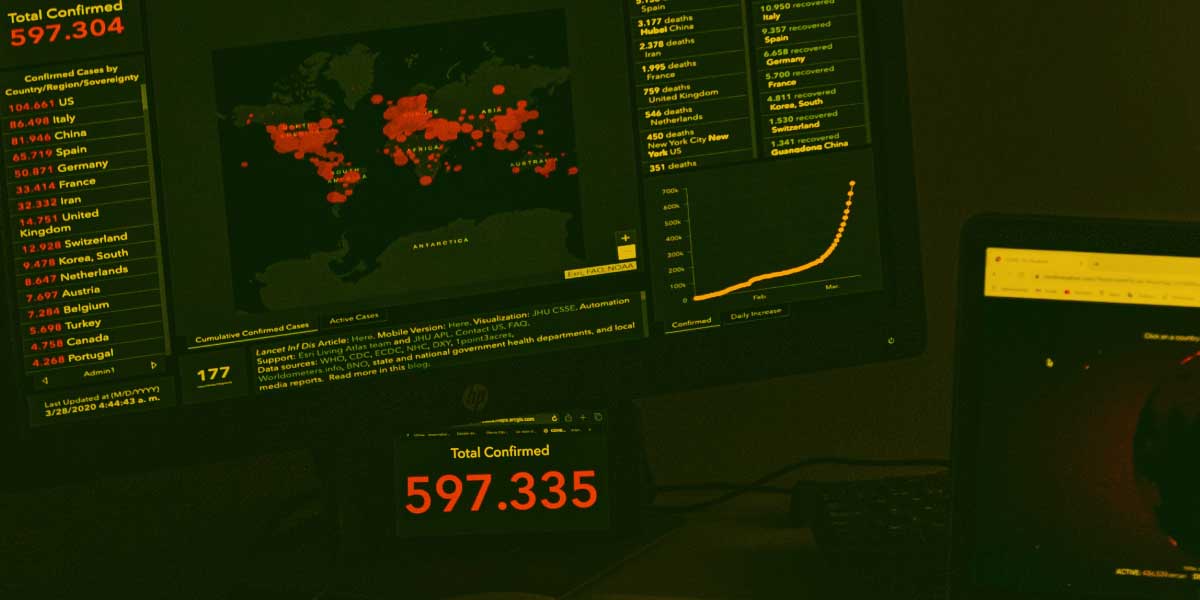
Threatening to halt this recovery are the ever-increasing successful cybersecurity attacks across various local government agencies including municipal utility authorities, departments of public works, infrastructure, education, and other township/county operations. Though many of these are related to sensitive information disclosures, phishing, and ransomware, there are targeted attacks impacting critical infrastructure systems. State government agencies of all sizes are exposed to these cyber threats, but few are equipped to provide rapid responses.
Here’s the list of fundamental cyber risk management imperatives when maturing digital transformation.
Implement Crawl-Walk-Run Strategy
Delays in management decisions during digital transformation rollout are often due to management misalignment and lack of accountability. Local government agencies should stop associating cyber risk as a technology function and realign it with business objectives to improve timely and adequate responses to security events. Dismantling monolithic cybersecurity and compliance activities and replacing them with activities that are distributed for ideal responsiveness reduces friction between stakeholders. Constant improvements to program maturity can be achieved through continuous monitoring of security and compliance posture while keeping control volatility to a minimum.
Manage Technical Debt
Local government agencies taking the fastest course to meet business process changes are accumulating technical debt and thereby increasing security exposure to opportunistic threat actors. Rapid response to cybersecurity events while managing technical debt requires complementing on-demand security assessments, hardware refreshes, software upgrades, and removal of unsupported/end-of-service-life systems. Incorporating security by design paradigm into digital resiliency initiatives ensures cyber risk analysts are not chasing irrelevant or non-contextual weaknesses. DevSecOps and Zero Trust architecture concepts have proven to accelerate security and compliance considerations and should be applied during the digital transformation journey.
Modernize Privileged Access
Cybersecurity controls for privileged users who are defined as users with greater entitlements as compared to others, should be re-engineered to utilize modern omnichannel capabilities. Adopting enhanced user access controls at state and local government agencies requires securing user relationships and maintaining activities’ traceability and auditing.
The one-size-fits-all cybersecurity controls approach at local state government agencies has failed to consider dynamically changing user characteristics and disparate agency responsibilities. Digital transformation at these entities will require identity management and access control systems to make rapid control decisions based on dynamic human and non-human (aka bots) attributes including location, business operating timeframes, toxic access combinations, device, and user type.
Maintain Continuous Monitoring:
Improving response time for cybersecurity alerts before becoming incidents during digital transformation can only be achieved by maintaining a practitioner-level understanding of cybersecurity controls and their continuous monitoring. Security by trust without verification impedes companies from achieving strategic objectives. Whether homegrown or on-premises hosted or Cloud, cybersecurity standards should be constantly updated to measure and maintain control effectiveness. Directives from multiple governance agencies including the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and National Security Agency (NSA) have defined cybersecurity event reporting requirements for state and local government agencies. Adopting these standards should be non-negotiable for foundational cybersecurity controls including timely patching, vulnerability assessments on updates and upgrades, privileged access management, adaptive authentication, encryption and periodic backup.
In Conclusion:
Cyber risk management maturity journey during digital transformation begins with justifying incremental cybersecurity investments by adopting modular capabilities that are distributed for optimal responsiveness. An effective cyber risk program implements contextual activities to constantly monitor controls, measures controls effectiveness, and adapts to detect scenarios of risk with full stakeholder transparency.